Spring Application Context
What is ApplicationContext?
According to the Spring document,
The
org.springframework.beansandorg.springframework.contextpackages are the basis for Spring Framework’s IoC container. TheBeanFactoryinterface provides an advanced configuration mechanism capable of managing any type of object.ApplicationContextis a sub-interface ofBeanFactory. It adds:
Easier integration with Spring’s AOP features
Message resource handling (for use in internationalization)
Event publication
Application-layer specific contexts such as the WebApplicationContext for use in web applications.
In short, the BeanFactory provides the configuration framework and basic functionality, and the ApplicationContext adds more enterprise-specific functionality. The
ApplicationContextis a complete superset of theBeanFactoryand is used exclusively in this chapter in descriptions of Spring’s IoC container.
What is IoC container?
It's the ApplicationContext.
What is bean?
In Spring, the objects that form the backbone of your application and that are managed by the Spring IoC container are called beans. A bean is an object that is instantiated, assembled, and managed by a Spring IoC container. Otherwise, a bean is simply one of many objects in your application. Beans, and the dependencies among them, are reflected in the configuration metadata used by a container.
Overview of the ApplicationContext
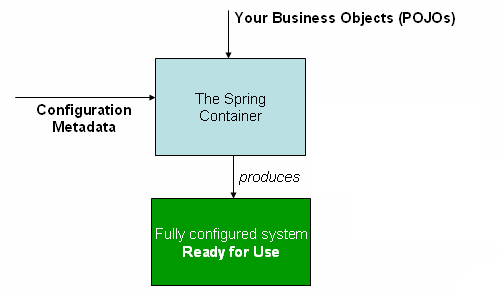
The Spring ApplicationContext represents the IoC container, and is responsible for instantiating, configuring, and assembling the beans. The container will read the configuration meta data from configuration file and Java annotations, or Java code. Then understand what objects need to instantiate, configure, and assemble.
There are several implementations of ApplicationContext supplied with Spring, including,
-
Standalone application context
- ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
- FileSystemXmlApplicationContext
- GenericXmlApplicationContext
-
GenericGroovyApplicationContext
Groovy based bean configuration. For example,
Groovybeans { dataSource(BasicDataSource) { driverClassName = "org.hsqldb.jdbcDriver" url = "jdbc:hsqldb:mem:grailsDB" username = "sa" password = "" settings = [mynew:"setting"] } sessionFactory(SessionFactory) { dataSource = dataSource } myService(MyService) { nestedBean = { AnotherBean bean -> dataSource = dataSource } } } -
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
Annotation based bean configuration.
-
GenericApplicationContext
The most flexible application context, in combination with reader delegates. For example,
JavaGenericApplicationContext context = new GenericApplicationContext(); new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(context).loadBeanDefinitions("services.xml", "daos.xml"); new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(context).scan("package"); context.refresh() // get the bean ExampleBean bean = context.getBean("exampleBean", ExampleBean.class);
-
Web Application context
- XmlWebApplicationContext
- AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext
- GroovyWebApplicationContext
- GenericWebApplicationContext
-
Servlet (for configuring servlet severs)
-
AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext
There are two AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContexts.
- One extends GenericWebApplicationContext, added since 2.2.0
- Another one extends ServletWebServerApplicationContext
-
XmlServletWebServerApplicationContext
-
The following diagram show the classes relationship of the application context.